In many transportation simulation applications including ITS,
behavioral responses of individual travelers are important. This
implies that simulating individual travelers directly may be useful.
Such a microscopic simulation, consisting of many intelligent
particles (
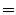
agents), is an example of a multi-agent simulation.
For ITS applications, it would be useful to simulate large
metropolitan areas, with 10 million travelers or more. Indeed, when
using parallel computing and efficient implementations, multi-agent
simulations of transportation systems of that size are feasible, with
computational speeds of up to 300 times faster than real time. It is
also possible to efficiently implement the simulation of day-to-day
agent-based learning, and it is possible to make this implementation
modular and essentially ``plug-and-play''. Unfortunately, these
techniques are not immediately applicable for within-day replanning,
which would be paramount for ITS. Alternative techniques, which allow
within-day replanning also for large scenarios, are discussed.
![]() Kai Nagel,
Kai Nagel,![]() and Bryan Raney
and Bryan Raney![]()
![]() Corresponding author
Corresponding author
![]() Institute for Computational Science (ICoS),
Institute for Computational Science (ICoS),
![]() Institute for Transportation Planning and Systems (IVT),
Institute for Transportation Planning and Systems (IVT),
![]() Transport Systems Planning and Transport Telematics,
Transport Systems Planning and Transport Telematics,